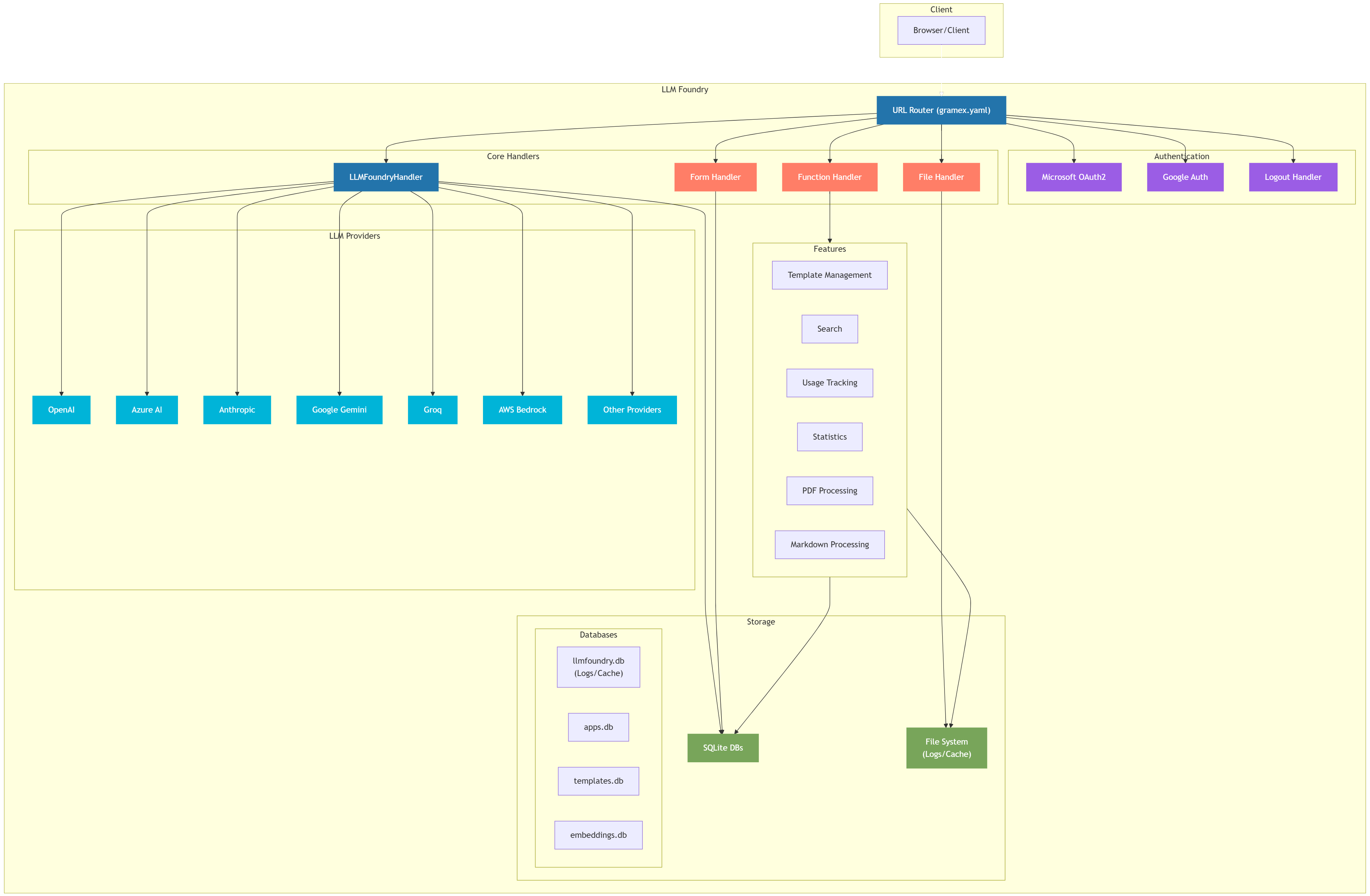
Architecture
Here's the LLM Foundry architecture.
graph TB
subgraph Client
Browser["Browser/Client"]
end
subgraph "LLM Foundry"
Router["URL Router (gramex.yaml)"]
subgraph "Authentication"
MSAuth["Microsoft OAuth2"]
GoogleAuth["Google Auth"]
Logout["Logout Handler"]
end
subgraph "Core Handlers"
LLMHandler["LLMFoundryHandler"]
FileH["File Handler"]
FormH["Form Handler"]
FuncH["Function Handler"]
end
subgraph "LLM Providers"
OpenAI["OpenAI"]
Azure["Azure AI"]
Anthropic["Anthropic"]
Gemini["Google Gemini"]
Groq["Groq"]
Bedrock["AWS Bedrock"]
Others["Other Providers"]
end
subgraph "Storage"
SQLite["SQLite DBs"]
subgraph "Databases"
LogDB["llmfoundry.db<br>(Logs/Cache)"]
AppsDB["apps.db"]
TemplatesDB["templates.db"]
EmbeddingsDB["embeddings.db"]
end
FileSystem["File System<br>(Logs/Cache)"]
end
subgraph "Features"
Templates["Template Management"]
Search["Search"]
Usage["Usage Tracking"]
Stats["Statistics"]
PDFProcess["PDF Processing"]
Markdown["Markdown Processing"]
end
end
%% Connections
Browser --> Router
Router --> MSAuth & GoogleAuth & Logout
Router --> LLMHandler & FileH & FormH & FuncH
LLMHandler --> OpenAI & Azure & Anthropic & Gemini & Groq & Bedrock & Others
LLMHandler --> SQLite
FileH --> FileSystem
FormH --> SQLite
FuncH --> Features
Features --> SQLite
Features --> FileSystem
%% Styling
classDef primary fill:#2374ab,stroke:#2374ab,color:white
classDef secondary fill:#ff7e67,stroke:#ff7e67,color:white
classDef storage fill:#78a55a,stroke:#78a55a,color:white
classDef auth fill:#9b5de5,stroke:#9b5de5,color:white
classDef provider fill:#00b4d8,stroke:#00b4d8,color:white
class Router,LLMHandler primary
class FileH,FormH,FuncH secondary
class SQLite,FileSystem storage
class MSAuth,GoogleAuth,Logout auth
class OpenAI,Azure,Anthropic,Gemini,Groq,Bedrock,Others provider
Security
LLM Foundry implements a comprehensive security model with multiple layers of authentication, authorization, and access control.
Authentication Mechanisms
1. Session Management
Refer gramex.yaml
app:
session:
samesite: "None" # Browser cookie security
secure: true # HTTPS only cookies
- Sessions are managed via encrypted cookies using a secure cookie secret
- HTTPS-only cookies prevent man-in-the-middle attacks
- SameSite and Secure cookie flags enabled
- Session IDs are changed on login to prevent session fixation attacks
2. Multi-Provider Authentication
The system supports multiple authentication providers:
- Microsoft Azure AD OAuth2 for enterprise authentication
- Google OAuth2 for Google Workspace users
Refer gramex.yaml
llmfoundry/login-ms:
pattern: /$YAMLURL/login-ms
handler: OAuth2
kwargs:
client_id: $LLMFOUNDRY_AZURE_CLIENT_ID
client_secret: $LLMFOUNDRY_AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET
llmfoundry-google-auth:
pattern: /$YAMLURL/googleauth/
handler: GoogleAuth
kwargs:
key: $LLMFOUNDRY_GOOGLE_KEY
secret: $LLMFOUNDRY_GOOGLE_SECRET
JWT-based authentication for token-based API access is supported. See the Token API.
3. API Key Authentication
When authenticating with LLM providers, multiple API key validation methods are supported, based on each provider's requirements:
- Bearer token authentication (OpenAI style)
- API key headers (Azure style)
- Custom headers (Anthropic, Google style)
Access Control
1. User Classification
Users are classified into:
- Internal users: Domains like @straive.com, @gramener.com
- External users: Specific allowed client domains
- Each group has different access levels and capabilities
2. Rate Limiting
- Error rate limiting (5 errors per minute per user)
- API request rate limiting
- Automatic blocking of excessive requests
3. Authorization Rules
Pages and APIs can be protected with granular rules:
- User attribute checks
- Email domain validation
- Multiple allowed values for attributes
- Role-based access control
Security Best Practices
- HTTPS Enforcement
- Secure cookies
- HTTPS-only access
- SSL/TLS encryption
- Token Security
- JWT tokens with HS256 algorithm
- Token expiration and rotation
- Secure token validation
- Input Validation
- Request validation
- Authentication header validation
- Parameter sanitization
- Error Handling
- Graceful error handling
- Rate limiting of error responses
- Sanitized error messages
- Secure Storage
- Credentials stored in environment variables, deployed via CI/CD
- Environment variable usage
- Encrypted sensitive data
- Logging
- Secure request logging
- User action tracking
- Error monitoring